Demystifying the Trio: Difference Between AI Machine Learning and Deep Learning
We will discuss about the Differences between AI Machine Learning and Deep Learning. In the realm of technology, three terms often intertwine and cause confusion: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL). While they share a common goal of enabling machines to mimic human intelligence, each concept represents a distinct facet of the evolving technological landscape. This article aims to dissect the differences between AI Machine Learning and Deep Learning, shedding light on their unique characteristics and applications.
I. Understanding Artificial Intelligence (AI):
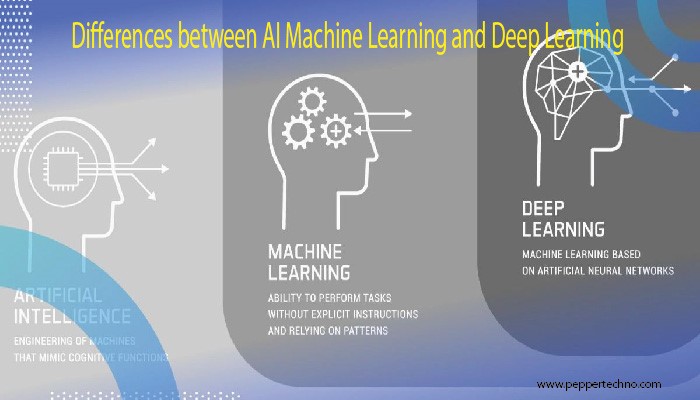
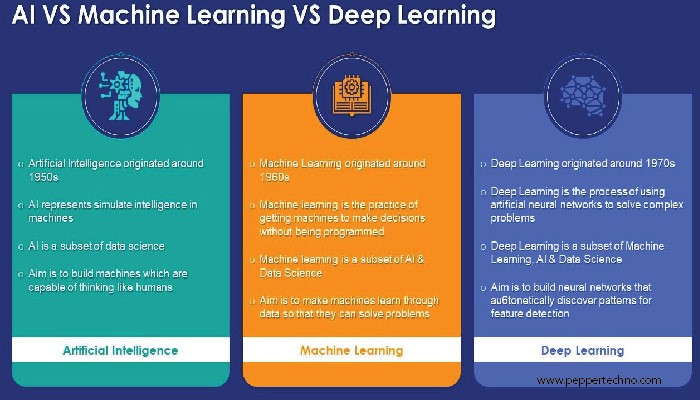
AI is the overarching field dedicated to creating intelligent machines capable of simulating human cognitive functions. The primary goal is to develop systems that can perceive reason, learn, and make decisions autonomously. Unlike traditional computer programming, AI systems are designed to adapt and improve over time based on experience.
Key Features of AI:
General vs. Narrow AI:
- General AI aspires to replicate human-like intelligence across a broad spectrum of tasks. It remains a theoretical concept and is yet to be fully realized.
- Narrow AI, on the other hand, focuses on excelling in specific tasks, such as language translation, image recognition, or game playing.
Rule-Based Systems:
- Early AI systems relied heavily on predefined rules and algorithms to perform tasks.
- The drawback was the lack of adaptability and scalability in handling complex scenarios.
II. Unraveling Machine Learning (ML):
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that empowers systems to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. ML algorithms allow machines to identify patterns, make predictions, and refine their models through continuous exposure to new information.
Key Features of Machine Learning:
Supervised Learning:
- In supervised learning, the model is trained on a labeled dataset, where the algorithm learns to map input data to corresponding output labels.
- Common applications include image recognition, speech recognition, and regression analysis.
Unsupervised Learning:
- Unsupervised learning involves working with unlabeled data, and the algorithm must find patterns or relationships within the data without predefined output labels.
III. Delving into Deep Learning (DL):
Deep Learning is a subset of machine learning that utilizes neural networks with multiple layers (deep neural networks) to model and process complex data. It is inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain, enabling the extraction of hierarchical features from data.
Key Features of Deep Learning:
Neural Networks:
- Deep Learning relies on neural networks, which are composed of interconnected layers of nodes (neurons).
- The depth of these networks allows them to automatically learn intricate hierarchical representations of data.
Feature Extraction:
- Deep Learning excels in automatic feature extraction from raw data, eliminating the need for manual feature engineering.
- This is particularly advantageous in tasks like image and speech recognition.
Complex Data Processing:
- DL algorithms excel in processing unstructured and large volumes of data, making them suitable for tasks like natural language processing and computer vision.
IV. Bridging the Gap: AI, ML, and DL in Harmony:
While AI Machine Learning and Deep Learning are distinct concepts, they often work in tandem to achieve remarkable results. The synergy between these technologies is evident in various applications, from voice assistants and recommendation systems to autonomous vehicles and medical diagnosis.
AI as the Umbrella:
- AI serves as the overarching umbrella, encapsulating both Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
- It involves the broader concept of creating intelligent systems capable of diverse tasks.
Machine Learning as the Engine:
- Machine Learning acts as the engine within AI, providing the algorithms and techniques to enable systems to learn from data.
- Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning are crucial components of ML.
Deep Learning for Complex Patterns:
- Deep Learning, being a subset of ML, excels in handling complex patterns and large datasets.
- Neural networks with multiple layers enhance the capacity to learn intricate representations.
Conclusion:
Understanding the distinctions between AI Machine Learning and Deep Learning is essential for navigating the rapidly evolving technological landscape. AI is the overarching concept, ML is the engine that enables learning from data, and DL leverages deep neural networks to process complex information. As these fields continue to advance, the collaborative efforts of AI, ML, and DL promise to reshape industries, enhance efficiency, and unlock unprecedented possibilities in the realm of intelligent machines.