UX Strategies for Human-Centered Design: Crafting Seamless Experiences
In the realm of design, particularly in the digital space, the user experience (UX) has emerged as a pivotal aspect that can make or break the success of a product or service. At the heart of effective UX lies the principle of human-centered design (HCD), a philosophy that prioritizes the needs, preferences, and behaviors of users in the design process. In this article, we delve into the world of UX strategies tailored specifically for human-centered design, exploring how designers can create seamless and intuitive experiences that resonate with users on a deeper level.
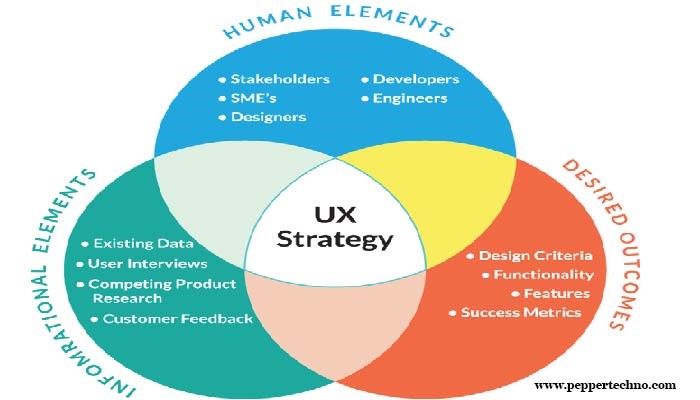
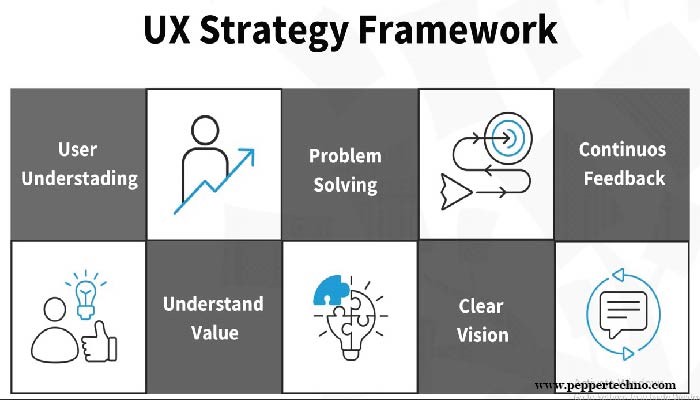
Understanding Human-Centered Design
Human-centered design revolves around the core idea of putting people first. It entails empathizing with users, defining their needs and challenges, ideating innovative solutions, prototyping designs, and continuously testing and iterating based on user feedback. By anchoring the design process in the lived experiences of real people, HCD aims to create products and services that are not only functional and efficient but also meaningful and emotionally resonant.
The Role of UX in Human-Centered Design
UX serves as the bridge between human-centered design principles and tangible design solutions. It encompasses a range of disciplines, including user research, interaction design, information architecture, and visual design, all geared towards creating cohesive and intuitive user experiences. Within the context of HCD, UX acts as a guiding framework that ensures designs are aligned with user needs and expectations at every stage of development.
Key Strategies for Human-Centered UX Design
User Research and Empathy Mapping: The foundation of human-centered UX design lies in understanding the needs, motivations, and pain points of users. Conducting thorough user research, which may involve interviews, surveys, and observational studies, allows designers to gain valuable insights into user behaviors and preferences. Empathy mapping, a technique that helps visualize user perspectives and emotions, enables designers to empathize more deeply with users and design solutions that address their underlying needs.
Persona Development: Once user research is complete, designers can create personas—fictional representations of typical users—to humanize their target audience and guide design decisions. Personas encapsulate key demographic information, behaviors, goals, and pain points of different user segments, providing a shared understanding of who the users are and what they seek to accomplish. By designing with specific personas in mind, designers can tailor experiences to meet the diverse needs of their user base.
Iterative Prototyping and Testing: Human-centered UX design is inherently iterative, with a continuous cycle of prototyping, testing, and refining designs based on user feedback. Prototyping allows designers to quickly visualize and test design concepts, ranging from low-fidelity wireframes to high-fidelity interactive prototypes. User testing, whether conducted through usability studies, A/B testing, or remote testing sessions, provides valuable insights into how real users interact with the design and highlights areas for improvement.
Design Thinking Workshops: Design thinking workshops bring cross-functional teams together to collaborate on solving complex problems from a user-centered perspective. By fostering creativity, empathy, and collaboration, these workshops encourage participants to think outside the box and generate innovative solutions that resonate with users. Through activities such as brainstorming, journey mapping, and rapid prototyping, teams can co-create solutions that address user needs holistically.
Accessibility and Inclusive Design: Human-centered UX design emphasizes inclusivity and accessibility, ensuring that products and services are usable by people of all abilities. Designing with accessibility in mind—from using clear typography and color contrast to providing alternative text for images—ensures that everyone, regardless of disabilities, can access and navigate digital experiences seamlessly. Inclusive design goes beyond compliance with standards and regulations, aiming to create experiences that are inherently usable and welcoming to diverse user groups.
Case Studies in Human-Centered UX Design
To illustrate the application of human-centered UX design strategies in real-world contexts, let’s explore two case studies: the redesign of a banking app and the development of a healthcare portal.
Case Study 1: Banking App Redesign
Challenge: A leading bank seeks to overhaul its mobile banking app to improve usability and enhance customer satisfaction.
Solution: By conducting user interviews and usability testing, the design team identifies pain points such as complex navigation and lack of personalization. Based on these insights, they streamline the app’s navigation, introduce personalized recommendations based on user preferences, and enhance accessibility features for visually impaired users. Through iterative prototyping and user testing, the team refines the design to ensure a seamless and intuitive banking experience for users of all demographics.
Case Study 2: Healthcare Portal Development
Challenge: A healthcare provider aims to develop an online portal that allows patients to schedule appointments, access medical records, and communicate with healthcare providers remotely.
Solution: Through ethnographic research and co-design workshops with patients and healthcare professionals, the design team uncovers user needs such as ease of use, privacy, and seamless integration with existing workflows. They design a user-friendly portal interface with intuitive navigation, clear communication channels, and robust security features. Usability testing with diverse user groups validates the effectiveness of the design in meeting user needs and identifies areas for further refinement.
Conclusion
In an increasingly digital world, human-centered UX design has become indispensable for creating products and services that resonate with users on a profound level. By prioritizing empathy, collaboration, and iterative refinement, designers can craft seamless and intuitive experiences that delight users and drive business success. By embracing human-centered design principles and leveraging UX strategies tailored to user needs, organizations can differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace and build enduring relationships with their customers.